The Binding or Combining of Rows with the rbind()-function in R
rbind() stands for row binding. In simpler terms joining of multiple rows to form a single batch. It may include joining two data frames, vectors, and more.
About rbind()-function in R Programming
This article will talk about the uses and applications of rbind() function in R programming.
Without wasting much time, let’s roll into the topic!!!
Syntax of the rbind()-function in R
rbind(): The rbind or the row bind function is used to bind or combine the multiple group of rows together.
rbind(x,x1)
Where:
X = the input data.
X1 = The data need to be binded.
The Idea of Binding Rows Using the rbind()-function in R
The idea of binding or combing the rows of multiple data frames is highly beneficial in data manipulation.
The below diagram will definitely get you the idea of working the rbind() function.
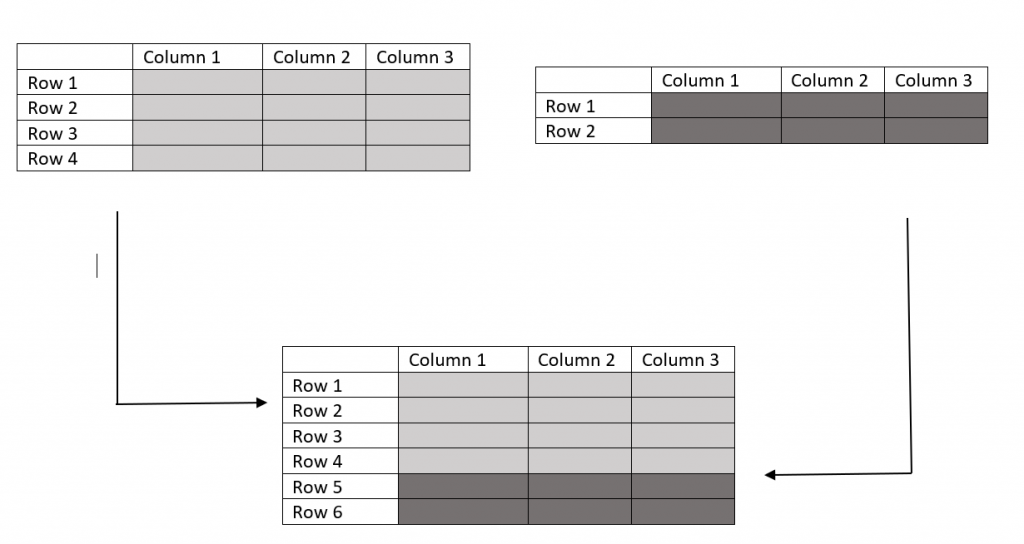
Rbind In R
You can see that how rows of different data frames will bound/combined by the rbind() function.
Implementing the rbind()-function in R
As you know that rbind() function in R used to bind the rows of different groups of data.
In this section, let’s try to construct a simple data frames and bind them using rbind() function.
#creating a data frame
Student_details<-c("Mark","John","Fredrick","Floyd","George")
Student_class<-c("High school","College","High school","High school","College")
df1<-data.frame(Student_class,Student_details)
df1
The above code will construct a simple data frame presenting student details and names.
Student_class Student_details
1 High school Mark
2 College John
3 High school Fredrick
4 High school Floyd
5 College George
Well, now we have a dataframe of 5 rows. Let’s create another data frame.
#creating a dataframe
Student_details<-c("Bracy","Evin")
Student_class<-c("High school","College")
Student_rank<-c("A","A+")
df2<-data.frame(Student_class,Student_details,Student_rank)
df2
Well, now we have 2 data frames of different row counts (df1 and df2). Let’s use the rbind() function to bind the above 2 data frames into a single data frame.
Let’s see how it works.
You won’t believe that the whole binding process will require just a line of code.
#binds rows of 2 input data frames
rbind(df1,df2)
The resultant data frame will be a bonded version of both data frames as shown in the above output.
Binding Two Data Frames of Unequal Length Using bind() Function
Well, in the previous section, we have combined the two row groups together.
In this section, we are going to combine two data sets together using the rbind function in R.
#creates the data frame
Student_details<-c("Mark","John","Fredrick","Floyd","George")
Student_class<-c("High school","College","High school","High school","College")
df1<-data.frame(Student_class,Student_details)
df1
Student_class Student_details
1 High school Mark
2 College John
3 High school Fredrick
4 High school Floyd
5 College George
#creats the data frame
Student_details<-c("Bracy","Evin")
Student_class<-c("High school","College")
Student_rank<-c("A","A+")
df2<-data.frame(Student_class,Student_details,Student_rank)
df2
Student_class Student_details Student_rank
1 High school Bracy A
2 College Evin A+
rbind(df1,df2)
Error in rbind(deparse.level, ...) :
numbers of columns of arguments do not match
Oh wait, what happened? Why the function is throwing an error?
If you read the lines in the error, it is stating that the number of columns is not matching.
We have 2 columns in ‘df1’ and 3 columns in ‘df2’.
Worry not! we have got the bind_rows() function which will assist us in these scenarios.
The bind_rows() Function to Bind Uneven Data Sets
bind_rows() is a function which is a part of dplyr package. We need to import the dplyr package first to execute this function.
We are using the same data frames present in the above section i.e df1 and df2. Let’s see how it works.
#install required packages
install.packages('dplyr')
#import libraries
library(dplyr)
#bind the rows
bind_rows(df1,df2)
Student_class Student_details Student_rank
1 High school Mark <NA>
2 College John <NA>
3 High school Fredrick <NA>
4 High school Floyd <NA>
5 College George <NA>
6 High school Bracy A
7 College Evin A+
you can now see that the bind_rows function has combined these two unequal datasets in terms of columns. The empty spaces will be marked as <NA>.
Binding Two Data Sets Using the rbind()-function in R
In this section, we will be looking into the binding of two entire data sets in R.
Let’s see how it works.
We are going to use the BOD data set as it has only 6 rows and also you can easily observe the bound rows.
#binds two data sets
rbind(BOD,BOD)
Time demand
1 1 8.3
2 2 10.3
3 3 19.0
4 4 16.0
5 5 15.6
6 7 19.8
---------------
7 1 8.3
8 2 10.3
9 3 19.0
10 4 16.0
11 5 15.6
12 7 19.8
BOD dataset has 6 rows. As we are passing the data twice, the rbind() function will bind the same rows as shown above.
And also don’t forget that you have bind_rows() function as well.
#binds two different datasets
bind_rows(BOD,women)
Time demand height weight
1 1 8.3 NA NA
2 2 10.3 NA NA
3 3 19.0 NA NA
4 4 16.0 NA NA
5 5 15.6 NA NA
6 7 19.8 NA NA
7 NA NA 58 115
8 NA NA 59 117
9 NA NA 60 120
10 NA NA 61 123
11 NA NA 62 126
12 NA NA 63 129
13 NA NA 64 132
14 NA NA 65 135
15 NA NA 66 139
16 NA NA 67 142
17 NA NA 68 146
18 NA NA 69 150
19 NA NA 70 154
20 NA NA 71 159
21 NA NA 72 164
These are the examples which clearly show the working and applications of the bind() and bind_rows functions.
I hope these illustrations helped you in understanding these functions.
Binding Multiple Rows Groups in R
In this section, we will be focusing on binding multiple (more than 2) row groups using the function rbind(). Let’s see how it works.
#binds rows of 3 data sets
bind_rows(BOD,women,ToothGrowth)
Time demand height weight len supp dose
1 1 8.3 NA NA NA <NA> NA
2 2 10.3 NA NA NA <NA> NA
3 3 19.0 NA NA NA <NA> NA
4 4 16.0 NA NA NA <NA> NA
5 5 15.6 NA NA NA <NA> NA
6 7 19.8 NA NA NA <NA> NA
7 NA NA 58 115 NA <NA> NA
8 NA NA 59 117 NA <NA> NA
9 NA NA 60 120 NA <NA> NA
10 NA NA 61 123 NA <NA> NA
11 NA NA 62 126 NA <NA> NA
12 NA NA 63 129 NA <NA> NA
13 NA NA 64 132 NA <NA> NA
14 NA NA 65 135 NA <NA> NA
15 NA NA 66 139 NA <NA> NA
16 NA NA 67 142 NA <NA> NA
17 NA NA 68 146 NA <NA> NA
18 NA NA 69 150 NA <NA> NA
19 NA NA 70 154 NA <NA> NA
20 NA NA 71 159 NA <NA> NA
Observe, how all three datasets were bonded or combined by the bind_rows() function in R. This is the beauty of bind_rows() function.
These 2 functions have endless applications in data manipulation in R programming.
Wrapping Up
The rbind()-function in R and the bind_rows()-function are the most useful functions when it comes to data manipulation.
You can easily bind two data frames of the same column count using the rbind()-function in R.
In the same way, if the data frames have unequal column counts, you can use the bind_rows() function along with dplyr package.
Well, That’s all for now, Happy binding!!! The Binding or Combining of Rows with the rbind()-function in R


