How to Install TestDisk in Linux and Recover Deleted Files
Ever stuck in a situation where you accidentally deleted a file? In this tutorial, we’ll go over how to install TestDisk in Linux and recover deleted files.
In this tutorial, I’ll be using an Ubuntu server to work with, but even if you are on any other distribution, you can follow the same steps. The only thing that will be different is the package manager used for installation.
Install TestDisk on Linux
The testdisk package is available on all the major Linux distributions and can be easily downloaded with the use of the default package manager. Here, I’ve listed down the distro-specific commands to install testdisk on Linux.
Install TestDisk on Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt -y install testdisk
We’re using the apt package manager instead of the apt-get since that’s the new package manager for Ubuntu/Debian.
Install TestDisk on Red Hat and CentOS 7
yum install epel-release
yum update
yum install testdisk
Install TestDisk on Red Hat and CentOS 8
yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
yum update
yum install testdisk
You need to also enable/install the EPEL repository. The EPEL repository is an additional package repository that provides easy access to install packages for commonly used software.
To know more about the EPEL repository, visit the official page.
Install TestDisk on Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S testdisk
Install TestDisk on Fedora
sudo dnf install testdisk
How To Recover Deleted Files in Linux?
Now that you have the testdisk utility installed, it’s time to use it to recover our deleted files or partitions.
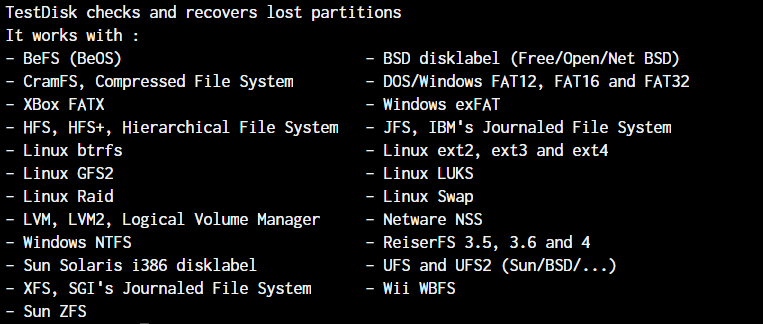
Partition Types TestDisk Works With
Testdisk works with the following partition types:
stat -f
df -T
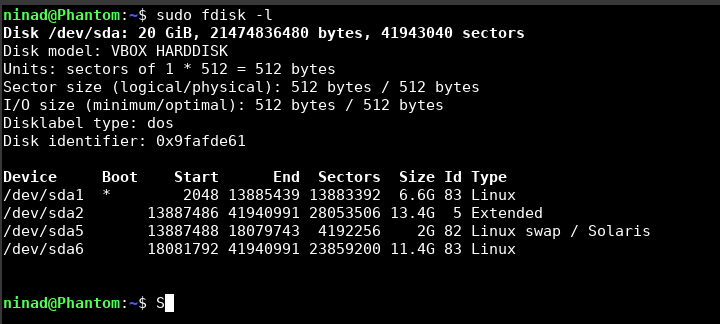
fdisk -l
Either of the commands above will give you the filesystem type information.
1. Starting TestDisk and Configuring Where it Runs
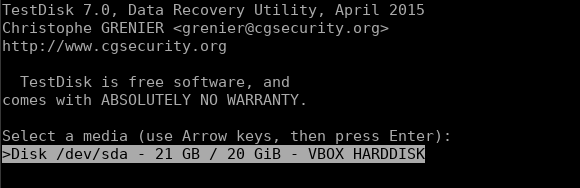
In your terminal, simply enter the command testdisk to run the utility and you’ll be greeted with the below prompt. You can select the appropriate disk drive that you want to recover files on.
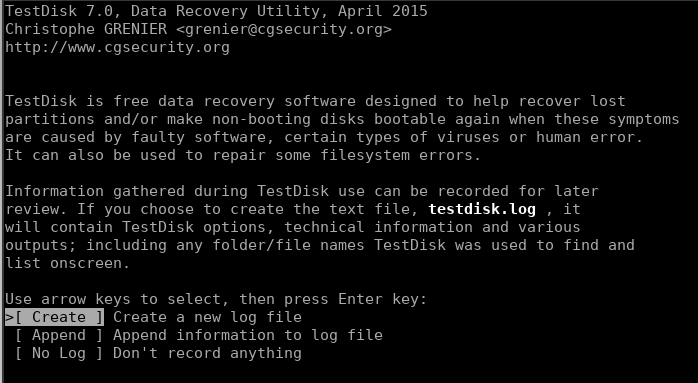
If its the first time you’re running this utility, it will give you an option to create a log file on the welcome screen. You can select create and just move ahead with the defaults.
The next screen asks you to select the disk drive/partition:
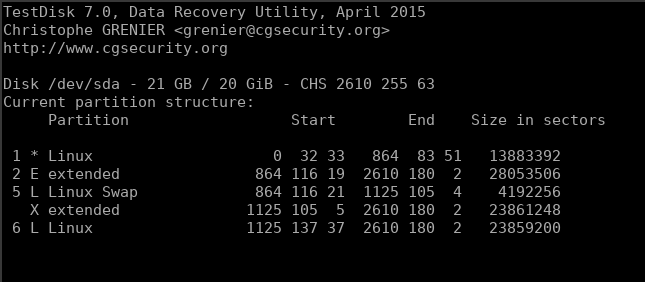
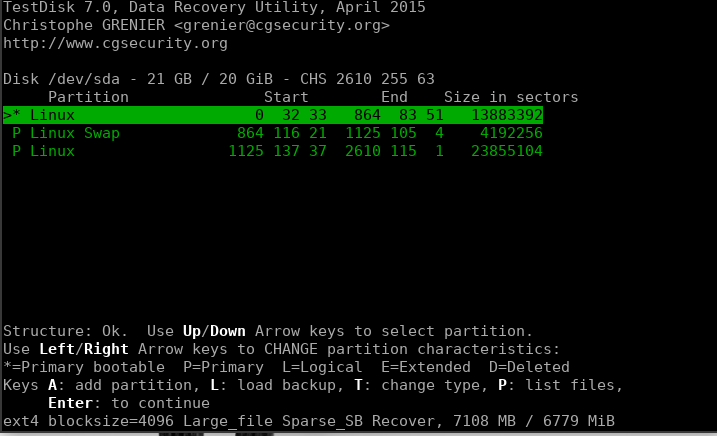
2. Selecting and Analyzing the Partition
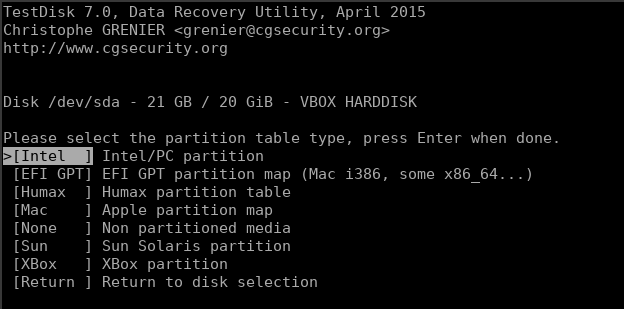
Once you’ve selected the right partition, you will be asked to select the partition type.
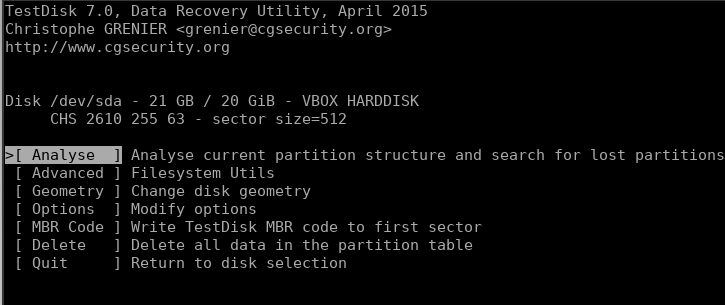
It should auto-select the correct partition type, but if it doesn’t, make sure you select the correct type. Once that’s done, you’ll be given a menu of options out of which we need to go ahead with “Analyse” to search for lost data.
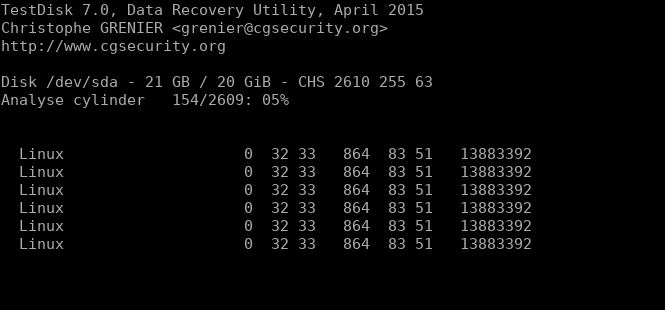
You can go with “Quick Search” or “Deeper Search” as it fits your needs and let the search run until it has scanned all the inodes.
3. Scanning the Partition for Deleted Files
Conclusion
Well, there you have it. You’ve learned how to recover deleted files in Linux! Go ahead and explore this utility more on a virtual machine to get a hang of it before using it in real-life situations so you know exactly how to work with it on an advanced scale.
We hope you’ve understood the use of the testdisk utility in Linux and know how to use it now. If you have any questions, let us know in the comments below.