File Size in Python
The os module in Python provides an efficient way to obtain file size. By using the stat() function, we can retrieve various file-related information. One of the key properties of this function is st_size, which gives the file size in bytes. This tutorial demonstrates a simple program to calculate file size in both bytes and megabytes. Additionally, it explores the limitations of the dir_fd argument in the stat() function when used on Mac OS.
File Size in Python: Basic Implementation
The Python os module provides the stat() function, where the file name is passed as an argument. The function returns a tuple structure containing the file information. Below is an example program that calculates and prints the file size in bytes and megabytes.
# get file size in python
import os
file_name = "/Users/pankaj/abcdef.txt"
file_stats = os.stat(file_name)
print(file_stats)
print(f'File Size in Bytes is {file_stats.st_size}')
print(f'File Size in MegaBytes is {file_stats.st_size / (1024 * 1024)}')
Output
Below is the output of the above program:
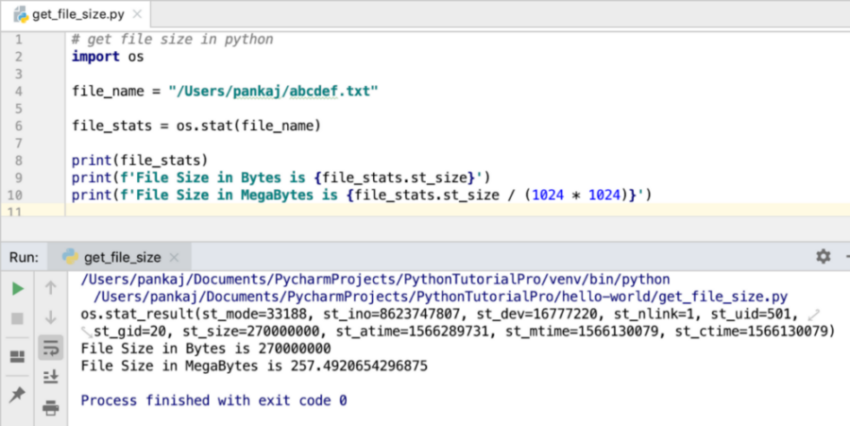 If you look at the
If you look at the stat() function, you can pass two additional arguments: dir_fd and follow_symlinks. However, these arguments are not implemented for Mac OS. The next example demonstrates this limitation.
File Size in Python: Relative Path Example
Here is an updated program where a relative path is used. Note that this throws a NotImplementedError on Mac OS.
# get file size in python
import os
file_name = "abcdef.txt"
relative_path = os.open("/Users/pankaj", os.O_RDONLY)
file_stats = os.stat(file_name, dir_fd=relative_path)
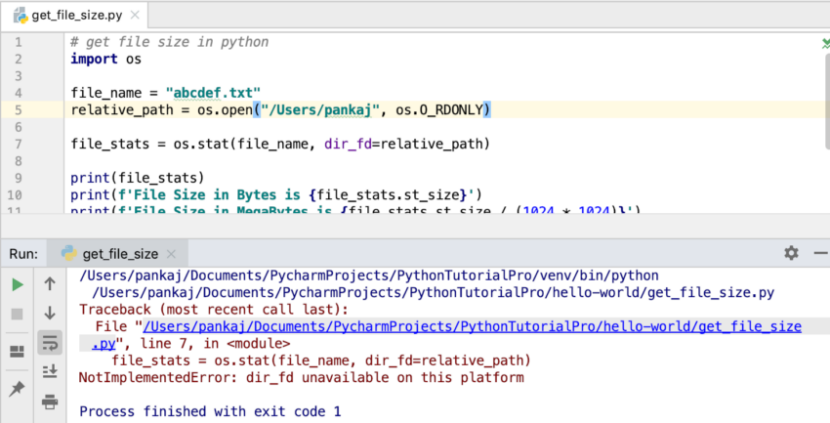
Output
Below is the output of the above program:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/Users/pankaj/.../get_file_size.py", line 7, in file_stats = os.stat(file_name, dir_fd=relative_path) NotImplementedError: dir_fd unavailable on this platform
Conclusion
Calculating file size in Python is straightforward using the os module’s stat() function. The property st_size allows us to determine the size of a file in bytes, and with simple arithmetic, we can convert it to megabytes. However, developers need to be aware of platform-specific limitations, as demonstrated with the dir_fd argument, which is not available on Mac OS. By understanding these nuances, developers can write more robust and portable Python scripts. This tutorial highlights the potential of Python for efficient file handling while cautioning about system-specific constraints.


